Chapter 6 - Refraction of light
1. Fill in the blanks and Explain the completed sentences.
a. Refractive index depends on the …………. of light.
Ans: velocity
Explanation: The refractive index of a medium is inversely proportional to the velocity of light, which means the refractive index of a medium rises and the speed of light going through that medium decreases.
b. The change in ……………. of light rays while going from one medium to another is called refraction.
Ans: direction
Explanation: Light changes its direction when passing from one transparent medium to another transparent medium, which is called refraction of light.
2. Prove the following statements.
a. If the angle of incidence and angle of emergence of a light ray falling on a glass slab are i and e respectively, prove that, i = e.
Ans:
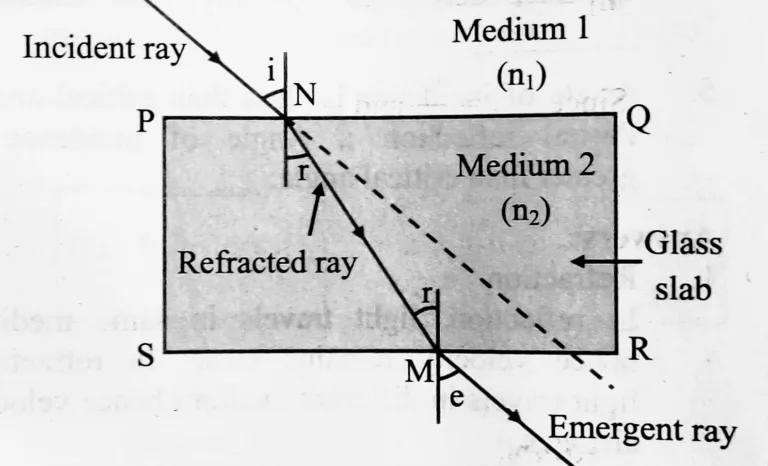
From figure,
i = angle of incidence,
r = angle of refraction,
e = angle of emergence.
At point N, using Snell’s law, we get,
\(_{glass}\) n \(_{air}\) = \(\large \frac {sin\,i}{sin\,r} \) …(1)
At point M, using Snell’s law, we get,
\(_{air}\) n \(_{glass}\) = \(\large \frac {sin\,r}{sin\,e} \) …(2)
But, \(_{glass}\) n \(_{air}\) = \(\large \frac {1}{_{air} n _{glass}} \)
∴ \(\large \frac {sin\,i}{sin\,r} \) = \(\large \frac {1}{\frac {sin\,r}{sin\,e}} \)
∴ \(\large \frac {sin\,i}{sin\,r} \) = \(\large \frac {sin\,e}{sin\,r} \)
∴ sin i = sin e
∴ ∠i = ∠e
Hence, for the refraction of light through a glass slab, angle of incidence is equal to angle of emergence, i.e., i = e.
b. A rainbow is the combined effect of the refraction, dispersion, and total internal reflection of light.
Ans:

(i) The rainbow appears in the sky after a rainfall.
(ii) Water droplets present in the atmosphere act as small prisms.
(iii) When sunlight enters these water droplets, it gets refracted and dispersed.
(iv) This dispersed light gets totally reflected inside the droplet and is again refracted while coming out of the droplet.
(v) As a combined effect of all these phenomena, the seven coloured rainbow is observed.
3. Mark the correct answer in the following questions.
A. What is the reason for the twinkling of stars?
(a) Explosions occurring in stars from time to time
(b) Absorption of light in the earth’s atmosphere
(c) Motion of stars
(d) Changing refractive index of the atmospheric gases
Ans: Option (d) – Changing refractive index of the atmospheric gases.
B. We can see the Sun even when it is little below the horizon because of
(a) Reflection of light
(b) Refraction of light
(c) Dispersion of light
(d) Absorption of light
Ans: Option (b) – Refraction of light
C. If the refractive index of glass with respect to air is 3/2, what is the refractive index of air with respect to glass?
(a) \(\large \frac {1}{2}\)
(b) 3
(c) \(\large \frac {1}{3}\)
(d) \(\large \frac {2}{3}\)
Ans: Option (d) – \(\large \frac {2}{3}\)
4. Solve the following examples.
a. If the speed of light in a medium is 1.5 × 10⁸ m/s, what is the absolute refractive index of the medium?
Given:
Speed of light in medium \(v_{2}\) = 1.5 × 10⁸ m/s
To find:
Absolute refractive index (n)
Solution:
We know that,
n = \(\large \frac {v_{1}}{v_{2}}\)
∴ n = \(\large \frac {3\, ×\,10⁸}{1.5\, ×\,10⁸}\) …[∵ \(v_{1}\) = velocity of light in vacuum = 3 × 10⁸ m/s ]
∴ n = 2
Ans: The absolute refractive index of the medium is 2.
b. If the absolute refractive indices of glass and water are \(\large \frac {3}{2}\) and \(\large \frac {4}{3}\) respectively, what is the refractive index of glass with respect to water?
Solution:
Let,
\(v_{1}\) is the velocity of light in vacuum
\(v_{2}\) is the velocity of light in glass
\(v_{3}\) is the velocity of light in water
∴ Absolute refractive index of glass,
i.e., refractive index of glass with respect to vacuum is,
\(n_{g}\) = \(\large \frac {v_{1}}{v_{2}}\) = \(\large \frac {3}{2}\) …(i)
And,
Absolute refractive index of water,
i.e., refractive index of water with respect to vacuum is,
\(n_{w}\) = \(\large \frac {v_{1}}{v_{3}}\) = \(\large \frac {4}{3}\) …(ii)
∴ Refractive index of glass with respect to water is,
\(_{g}\) n \(_{w}\) = \(\large \frac {v_{3}}{v_{2}}\)
∴ \(_{g}\) n \(_{w}\) = \(\large \frac {v_{1}}{v_{2}}\) × \(\large \frac {v_{3}}{v_{1}}\) …[Multiplying and dividing R.H.S. of equation by \(v_{1}\))
∴ \(_{g}\) n \(_{w}\) = \(\large \frac {3}{2}\) × \(\large \frac {3}{4}\) …[From equations (i) and (ii)]
∴ \(_{g}\) n \(_{w}\) = \(\large \frac {9}{8}\)
Ans: The refractive index of glass with respect to water is \(\large \frac {9}{8}\).
