Chapter 4 - History of Indian Arts
1. (A) Choose the correct option from the given options and complete the statement.
(1) The arts of painting and sculpting are ………..
(a) visual arts
(b) performing arts
(c) folk arts
(d) classical arts
Ans: Option (a) – visual arts
(2) The ………. saw the rise of Mathura school.
(a) Kushana period
(b) Gupta period
(c) Rashtrakuta period
(d) Maurya period
Ans: Option (a) – Kushana period
(B) Identify and write the wrong pair in the following set.
(1) Qutub Minar – Mehrauli
(2) Gol Gumbaz – Vijapur
(3) Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Railway Terminus – Delhi
(4) Taj Mahal – Agra
Ans: The wrong pair is:
Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Railway Terminus – Delhi
Explanation: Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Railway Terminus is located in Mumbai.
2. Write short notes.
(1) Art
Ans:
(i) When humans experience wisdom, emotions result in the form of beautiful creation, it is acknowledged as ‘Art’.
(ii) The artist’s power of imagination, sensibility, state of emotion are the crucial factors at the root of artistic creation.
(iii) It can be classified into two types: Visual arts and Performing arts. Also there are two distinct traditions of art, ‘Folk Art’ and ‘Classical Art’.
(2) Hemadpanti style
Ans:
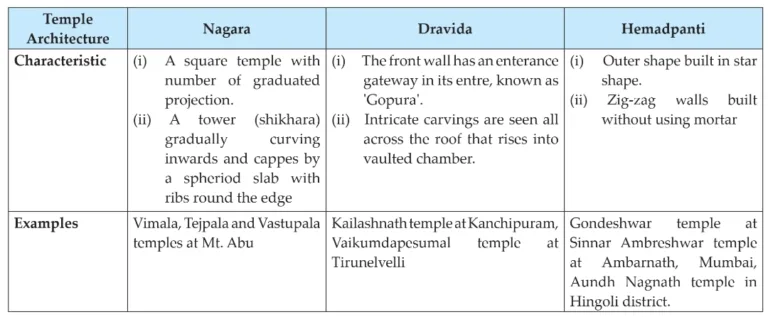
(i) The temples in Maharashtra built in 12th-13th centuries are known as Hemadpanti temples.
(ii) The outer walls of Hemadpanti temples are built in a star shape. In the star-shaped plan, the outer walls of the temple have a zig-zag design. This results in an interesting effect of alternating light and shadow.
(iii) The important characteristics of Hemadpanti temple is its masonry. The walls are built without using any mortar, by locking the stones by using the technique of tenon and mortise joints.
(iv) The Ambreshwar Temple at Ambernath near Mumbai, Gondeshwar temple at Sinnar near Nashik, Aundha Nagnath temple in the Hingoli district are a few finest examples of the Hemadpanti style.
(3) Maratha style of painting
Ans:
(i) Maratha paintings are an example of Art style. It was developed in the latter half of the 17th century CE.
(ii) This style consists of coloured paintings and they occur as murals and miniatures used in manuscripts.
(iii) Murals of Maratha style can be seen in the old wadas at places like Wai, Menavali and Satara in Maharashtra.
(iv) The Maratha style was influenced by the Rajput and European styles of painting.
(v) Paintings help us understand about the times in which it was developed such as lifestyle, attire, customs, etc.
3. Explain the following statements with reasons.
(1) An expert with a deep understanding of art history is required in the art market.
Ans:
(i) Art is an independent branch of knowledge.
(ii) It calls for special expertise to assess the exact value of an art object or to ensure that it is genuine.
(iii) So an expert with a deep understanding of art history is required in the art market.
(2) It is necessary to preserve the tradition like Chitrakathi, which is on the verge of extinction.
Ans:
(i) Chitrakathi is an antique tradition of 12th century CE.
(ii) It is the tradition of narrating stories from Ramayana or Mahabharata with the help of wooden puppets and paintings.
(iii) The pictures are drawn on paper using natural colours.
(iv) It takes 30-50 pictures to complete a single story and then it is passed on carefully from generation to generation.
(v) So it is necessary to preserve the tradition like Chitrakathi, which is on the verge of extinction.
4. Complete the following table.
Ans:
5. Answer the following questions in detail.
(1) Write in detail about folk styles of painting.
Ans:
(i) The tradition of folk style of paintings closely resembles the style of rock paintings.
(ii) Customs such as decorating the house walls and courtyards by drawing various figures and symbols or using panels of paintings to narrate stories has helped to develop regional styles of folk paintings.
(iii) The traditions of Warli painting and Pingul or Chitrakathi are amongst the finest examples of folk style paintings.
(2) Explain the characteristics of the Islamic architecture in India by giving examples.
Ans:
(i) In the medieval period, under the patronage of Muslim sultanates many styles of architecture, such as Persian, Central Asian, Arabic and pre-Islamic native Indian styles were blended together creating Islamic architecture in India.
(ii) The Qutub Minar was started in 12th century CE and completed in 13th century CE. It is 73 metres in height.
(iii) The Taj Mahal is looked upon as the paramount example of the beauty of Islamic Architecture.
(iv) The Gol Gumbaz, houses the burial of Md. Adilshah of Bijapur
(v) Inside the dome after which the building is named, there is a round gallery. Even a slight whisper by the person standing in this gallery can be heard everywhere.
(3) What kind of professional opportunities are available in the field of arts?
Ans: The opportunities of research available in the field of arts are:
(i) Art historians can work in the field of journalism.
(ii) They can also work as special experts to assess the exact value of an art object or to ensure that it is genuine.
(iii) They can also find professional opportunities as an expert in the field of Museums and Archives Management, Library Science and Information Technology, Archaeological Research, Indology etc.
(4) Observe the illustration of Warli painting on page 23 and write about:
(a) Depiction of nature
(b) Drawings of human figures
(c) Depiction of occupations
(d) Houses
Ans:
(a) Depiction of nature:
(i) Every symbol of Warli art has its own meaning and language.
(ii) The sacred nature of the trees is suggested by their soaring heights in relation to man and animals.
(iii) Nothing is static; the trees, the human figures, the birds challenge and respond to each other.
(iv) The harmony and balance depicted in these paintings is supposed to signify the harmony and balance of the universe.
(b) Drawings of human figures:
(i) Men and women in spiral form and concentric circular designs in Warli paintings symbolize the circle of life.
(ii) Human and animal bodies are represented by two triangles joined at the tip. The upper triangle depicts the trunk and the lower triangle the pelvis.
(c) Depiction of occupations:
(i) The picture shown is of a marriage ceremony. No occupation is depicted in the picture.
(ii) The painting shown is a famous traditional composition known as ‘Lagnacha chouk’.
(iii) Lagnacha chouk shows the preparations of marriage ceremonies like bringing water, setting up pandals and Tarapa Dance and their musical instruments.
(d) Houses:
(i) Since the picture is of a marriage ceremony, no houses are shown.
(ii) Depictions of the community is dance. The Tarapa dance where women and men entwine their arms together to create a sinuous chain is seen.
