Chapter 1 - Post World War Political Developments
1. (A) Choose the correct option from the given options and complete the statements.
(1) A system of independent and sovereign States –
(a) Political system
(b) International system
(c) Social system
(d) None of these
Ans: Option (b) – International system
(2) The main responsibility of the United Nations –
(a) to avoid war
(b) independence of colonies
(c) improving the economics of different nations
(d) disarmament
Ans: Option (a) – to avoid war
(3) The Cold War ended with this event
(a) Establishment of the United Nations
(b) Disintergration of the Soviet Russia
(c) Creation of Military Organisations
(d) Cuban Missile Crisis
Ans: Option (b) – Disintergration of the Soviet Russia
2. State whether the following statements are true or false. Give reasons for your answer.
(1) The League of Nations was established after the First World War.
Ans: The above statement is True.
Reason:
(i) The First World War caused a tremendous loss of life and property.
(ii) All the nations felt that such a war should not happen again and that some measures needed to be taken to achieve this end.
(iii) Out of this thinking, an international organisation called the League of Nations was established.
(2) The world became unipolar due to the Cold War.
Ans: The above statement is False.
Reason:
(i) At the end of the Second World War, America and the Soviet Union became competitors.
(ii) America and the Soviet Union, who were allies in war, formed rival military organisations.
(iii) Most countries in the world joined the power blocs headed by these two superpowers.
(iv) Thus, the world became bipolar due to the Cold War.
(3) The policies of Mikhail Gorbachev gave an impetus to democratisation.
Ans: The above statement is True.
Reason:
(i) The Soviet Union adopted the policy of opening up the economy.
(ii) The State loosened up its control of the economy.
(iii) The President of the Soviet Union, Mikhail Gorbachev, implemented the policies of Perestroika (Restructuring) and Glasnost (Openness).
(iv) Due to these policies, control over the media was reduced.
(v) Important changes took place in the political and economic spheres.
(vi) Thus, the policies of Mikhail Gorbachev gave an impetus to democratisation.
3. Explain the following concepts.
(1) Cold War
Ans:
(i) The concept of the Cold War is used to describe the condition where there is no actual war but there are such tensions in the circumstances that they may be responsible for causing war.
(ii) So, there is no open war between the two countries, but there was such tension in their relations that it seemed that a war would erupt at any time.
(2) Non-alignment
Ans:
(i) In the era of the Cold War, while the world was becoming bipolar, there were some nations, like India, that did not want to join the superpower rivalry.
(ii) Such nations decided to stay out of the Cold War rivalry. Their policy is known as non-alignment.
(3) Interdependence
Ans:
(i) Interdependence means that all countries in the world are dependent on each other.
(ii) Even a developed nation like America is not self-sufficient in all its needs.
(iii) So, however big, small, or prosperous a nation is, it is dependent on the other nations.
(iv) It is an important feature of the contemporary international system.
(4) Bipolarisation
Ans:
(i) During the era of the Cold War, America and the Soviet Union emerged as the superpowers and formed their military alliances.
(ii) Most countries in the world joined either of the two superpower blocs.
(iii) Such a division of the nations of the world into two groups is described as Bipolarisation.
(5) Globalisation
Ans:
(i) In the 1990s, after the end of the Cold War, trade and economic relations between countries became more open.
(ii) There was a free flow of capital, technology, labour, markets, and information across the world.
(iii) The boundaries between nations did not remain as sacrosanct as they were before.
(iv) There was a give and take of ideas among people all over the world. All these processes together are called Globalisation.
4. Write brief answers.
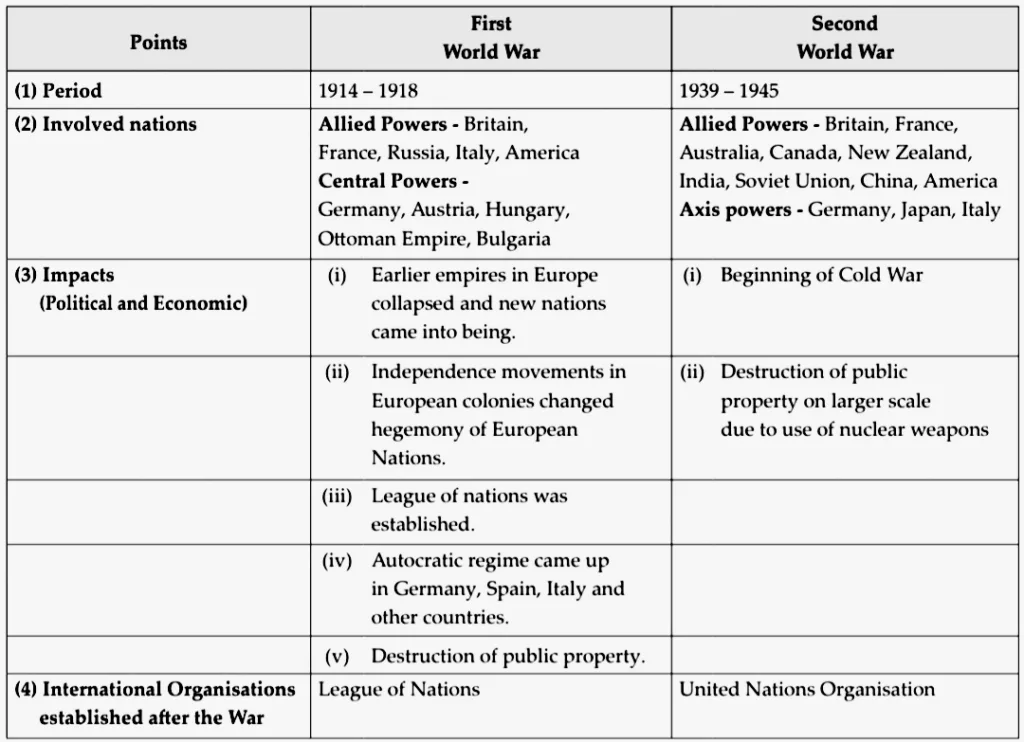
(1) Compare the First World War and the Second World War with the help of the following points :
Ans:
(2) What were the factors responsible for the end of the Cold War?
Ans: The factors responsible for the end of the Cold War are as follows:
(i) The Soviet Union adopted the policy of opening up the economy and loosening state control over it.
(ii) The then president of the Soviet Union, Mikhail Gorbachev, implemented the policies of Perestroika (Restructuring) and Glasnost (Openness). The Soviet economy and politics were restructured.
(iii) He reduced control over the press. This gave impetus to democracy in Russia.
(iv) The East European countries challenged ‘socialist’ governments. These countries broke free from the influence of the Soviet Union and adopted a democratic, capitalist path.
(v) The disintegration of the Soviet Union contributed to ending the Cold War.
(3) What major changes occured in global politics after the end of the Cold War?
Ans: The following major changes occurred in global politics after the end of the Cold War:
(i) Global politics became unipolar, with America remaining the only superpower.
(ii) An atmosphere conducive to the growth of trade and economic relations between and among nations emerged.
(iii) Capital, labor, market, technology, ideas, and information freely circulated throughout the world.
(iv) The idea of giving ‘aid’ to other nations fell behind as all nations of the world decided to give priority to trade relations.
(v) The description of a country that was opposed to another changed from ‘enemy nation’ to ‘rival nation’.
(vi) The responsibility of the United Nations has increased. It is now required to take concrete steps to maintain global peace and security.
(vii) The issues of environmental protection, fostering human rights, gender equality, and management of natural calamities have now acquired a global dimension.
