Chapter 6 - Bureaucracy
1. Identify if the following statements are correct or wrong and rewrite the wrong sentences in their correct form.
(1) In a parliamentary democracy, representatives elected by people and ministers bear the administrative responsibility.
Ans: Correct.
(2) Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) recruits candidates for civil services in Maharashtra.
Ans: Incorrect.
Correct statement: Maharashtra Public Service Commission recruits candidates for civil services in Maharashtra.
2. Explain the following statements with reasons.
(1) Reservation policy is followed even in civil services.
Ans:
(i) A part of the society comprising scheduled castes, scheduled tribes, women, other backward castes, and specially abled is termed the “weaker section” of the society.
(ii) It was essential to empower these weaker sections.
(iii) They were left out of civil services due to social inequality.
(iv) In order to establish social justice and provide opportunities to weaker sections of society, reservation policy is followed even in the civil service.
(2) It is necessary for civil servants to be politically neutral.
Ans:
(i) In Parliamentary democracy, in India, a new government comes in power after every five years. But the bureaucracy is permanent, i.e., it remains the same.
(ii) The bureaucracy is expected to implement the policies and decisions of the earlier government with the same efficiency and commitment.
(iii) Civil servants are expected to avoid taking a political stand and remain neutral while discharging their duties.
(iv) If civil servants work according to their political views, it will lead to chaos.
(v) Hence, they should be politically neutral.
3. Answer the following in 25-30 words.
(1) Explain the role of the ministers and civil servants in the efficient administration of the department.
Ans:
(i) The efficiency of a particular department depends upon the inter-relationship between the minister, his secretary, and his deputy secretary.
(ii) The decisions taken by the ministers are based on the necessary information provided by the bureaucracy.
(iii) The bureaucracy, i.e., civil servants, have complete information about the financial provisions for a particular scheme or plan and also about the history of successes and failures of policies.
Hence, if the ministers develop mutual trust and transparency with the civil servants, it will help in the efficient administration of the department.
(2) Explain how the bureaucracy provides stability to the political system.
Ans:
(i) The bureaucracy does the work of implementing decisions taken by the ministers.
(ii) Several important reforms introduced during the post-independence period have been effectively implemented by the bureaucracy.
(iii) It consistently provides services like water supply, public cleanliness, transport, electricity, etc. to the people and brings stability to their day-to-day lives.
(iv) It acts as an instrument of social transformation and democratization.
In this way, it gives stability to the political system.
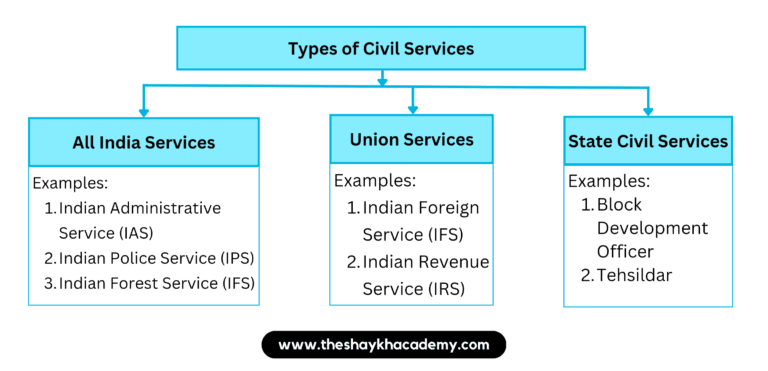
4. Complete the concept picture.
Ans:
5. Discuss characteristics of bureaucracy.
Ans: The bureaucracy is the administrative organisation working under the aegis of the union executive and is entrusted with the responsibility of the day-to-day business of a government.
(a) Permanent Mechanism:
(i) The bureaucracy constitutes the permanent executive of the government and is entrusted with the responsibility of some of the crucial functions that require consistency.
(ii) Example: maintenance of law and order, tax collection, environmental protection, etc.
(b) Political neutrality:
(i) The bureaucracy is expected to work impartially and fairly, regardless of the political party in power.
(ii) The new party forming the government will trust the bureaucracy with non-partisanship, thus fostering mutual trust and enabling both to work together for the public interest.
(iii) The All India Services (Conduct) Rules direct that an officer must not take part in politics.
(iv) He or she must not give election funds or assistance to any political party.
(c) Anonymity:
(i) Anonymity is an important characteristic that enables a civil servant to render advice impartially, frankly, and freely with the assurance that he or she is not dragged into the public debate.
(ii) The concerned minister is accountable for policy outcomes.
(iii) The All India Services (Conduct) Rules 1968 prescribe that the civil servant avoid occasions of self-publicity so that their anonymity is preserved.
