Pythagoras Theorem
Theorem :
In a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the remaining two sides.
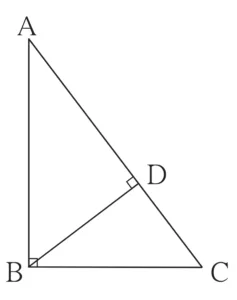
Given :
In ∆ABC,
∠ ABC = 90°
To prove :
AC² = AB² + BC²
Construction :
Draw perpendicular seg BD on side AC, such that A – D – C
Proof :
In right angled ∆ABC,
seg BD ⊥ hypotenuse AC …[By construction]
∴ ∆ABC ~ ∆ADB ~ ∆BDC …[By similarity of right angled triangles]
(i) ∆ABC ~ ∆ADB
\(\large \frac {AB}{AD}\) = \(\large \frac {AC}{AB}\) …[Corresponding sides are proportional]
∴ AB² = AC × AD …(i)
(ii) ∆ABC ~ ∆BDC
\(\large \frac {BC}{DC}\) = \(\large \frac {AC}{BC}\) …[Corresponding sides are proportional]
∴ BC² = AC × DC …(ii)
Adding equations (i) and (ii), we get,
AB² + BC² = AC × AD + AC × DC
∴ AB² + BC² = AC (AD + DC)
∴ AB² + BC² = AC (AC) …[A – D – C]
∴ AB² + BC² = AC²
i.e. AC² = AB² + BC²
Hence Proved.
