Basic Proportionality Theorem
Theorem :
If a line parallel to a side of a triangle intersects the remaining sides in two distinct points, then the line divides the sides in the same proportion.
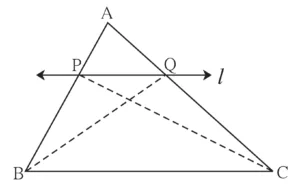
Given :
In ∆ABC,
line l || line BC and line l intersects AB and AC in points P and Q respectively.
To prove :
\(\large \frac {AP}{PB}\) = \(\large \frac {AQ}{QC}\)
Construction:
Draw seg PC and seg BQ
Proof :
∆APQ and ∆PQB have equal heights
∴ \(\large \frac {A (∆APQ)}{A (∆PQB)}\) = \(\large \frac {AP}{PB}\) … (I) [The ratio of areas of two triangles having equal heights, is equal to the ratio of their corresponding bases]
and \(\large \frac {A (∆APQ)}{A (∆PQC)}\) = \(\large \frac {AQ}{QB}\) … (II) [The ratio of areas of two triangles having equal heights, is equal to the ratio of their corresponding bases]
Now,
seg PQ is the common base of ∆PQB and ∆PQC
and seg PQ || seg BC
Hence ∆PQB and ∆PQC have equal heights
A(∆PQB) = A(∆PQC) ………. (III)
∴ \(\large \frac {A (∆APQ)}{A (∆PQB)}\) = \(\large \frac {A (∆APQ)}{A (∆PQC)}\) … [from (I), (II) and (III)]
∴ \(\large \frac {AP}{PB}\) = \(\large \frac {AQ}{QB}\) … [from (I) and (II)]
Hence proved
