Chapter 6 – Composition of matter
1. Choose the appropriate option and rewrite the following statements.
a. The intermolecular force is ________ in the particles of solid.
i. minimum
ii. moderate
iii. maximum
iv. indefinite
Ans: Option iii – maximum
b. Solids retain their volume even when external pressure is applied. This property is called ________.
i. plasticity
ii. incompressibility
iii. fluidity
iv. elasticity
Ans: Option ii – incompressibility
c. Matter is classified into the types mixture,compound and element, by applying the criterion ________.
i. states of matter
ii. phases of matters
iii. chemical composition of matter
iv. all of these
Ans: Option iii – chemical composition of matter
d. Matter that contain two or more constituent substances is called ________.
i. mixture
ii. compound
iii. element
iv. metalloid
Ans: Option i – mixture
e. Milk is an example of type of matter called ________.
i. solution
ii. homogeneous mixture
iii. heterogeneous mixture
iv. suspension
Ans: Option iii – heterogeneous mixture
f. Water, mercury and bromine are similar to each other, because three are ________.
i. liquids
ii. compounds
iii. nonmetals
iv. elements
Ans: Option i – liquids
g. Valency of carbon is 4 and that of oxygen is 2. From this, we understand that there are ________ chemical bond/bonds between the carbon atom and one oxygen atom in the compound-carbon dioxide.
i. 1
ii. 2
iii. 3
iv. 4
Ans: Option ii – 2
2. Identify the odd term out and explain.
a. Gold, silver, copper, brass
Ans: Brass
Reason: Brass is a mixture while others are elements.
b. Hydrogen, hydrogen peroxide, carbon dioxide, water vapour.
Ans: Hydrogen
Reason: Hydrogen is an element while others are compounds.
c. Milk, lemon juice, carbon, steel.
Ans: Carbon
Reason: Carbon is an element while others are mixtures.
d. Water, mercury, bromine, petrol.
Ans: Petrol
Reason: Petrol is an organic compound while others are inorganic compounds.
e. Sugar, salt, baking soda, blue vitriol.
Ans: Sugar
Reason: Sugar is an organic compound while others are inorganic compounds.
f. Hydrogen, sodium, potassium, carbon.
Ans: Hydrogen
Reason: Hydrogen is a gas while others are solids.
3. Answer the following question.
a. Plants synthesize glucose in sunlight with the help of chlorophyll from carbon dioxide and water and give away oxygen. Identify the four compounds in this process and name their types.
Ans:
(i) The four compounds in this process are mom glucose, chlorophyll, carbon dioxide and water.
(ii) Compounds and their types:
(a) Glucose – Organic compound
(b) Chlorophyll – Complex compound
(c) Carbon dioxide – Inorganic compound
(d) Water – Inorganic compound
b. In one sample of brass, the following ingredients were found : copper (70%) and zinc (30%). Identify the solvent, solute and solution from these.
Ans:
(i) The solvent is copper as it is present in high proportion in the solution.
(ii) The solute is zinc as it is present in less proportion in the solution.
(iii) The solution is brass as it is a homogeneous mixture of two metals.
c. Sea water tastes salty due to the dissolved salt. The salinity (the proportion of salts in water) of some water bodies Lonar lake – 7.9 %, Pacific Ocean 3.5 %, Mediterranean sea – 3.8 %, Dead sea – 33.7 %. Explain two characteristics of mixtures from the above information.
Ans:
(i) The proportion of salts (constituent substances) in the sea water (mixture) is different. That is, the proportion of constituent substances in a mixture can change.
(ii) The salinity of the sea water from different water bodies is due to the dissolved salts. That is, the properties of the constituent substances are retained in the mixture.
4. Give two examples each
a. Liquid element
Ans: Mercury (Hg), bromine (Br₂)
b. Gaseous element
Ans: Hydrogen (H₂), oxygen (O₂)
c. Solid element
Ans: Copper (Cu), aluminium (Al)
d. Homogeneous mixture
Ans: Air, sea water
e. Colloid
Ans: Fog, smoke
f. Organic compound
Ans: Glucose, urea
g. Complex compound
Ans: Chlorophyll, cyanocobalamine
h. Inorganic compound
Ans: Common salt, limestone
i. Metalloid
Ans: Silicon (Si), germanium (Ge)
j. Element with valency 1
Ans: Hydrogen, chlorine
k. Element with valency 2
Ans: Oxygen, sulphur
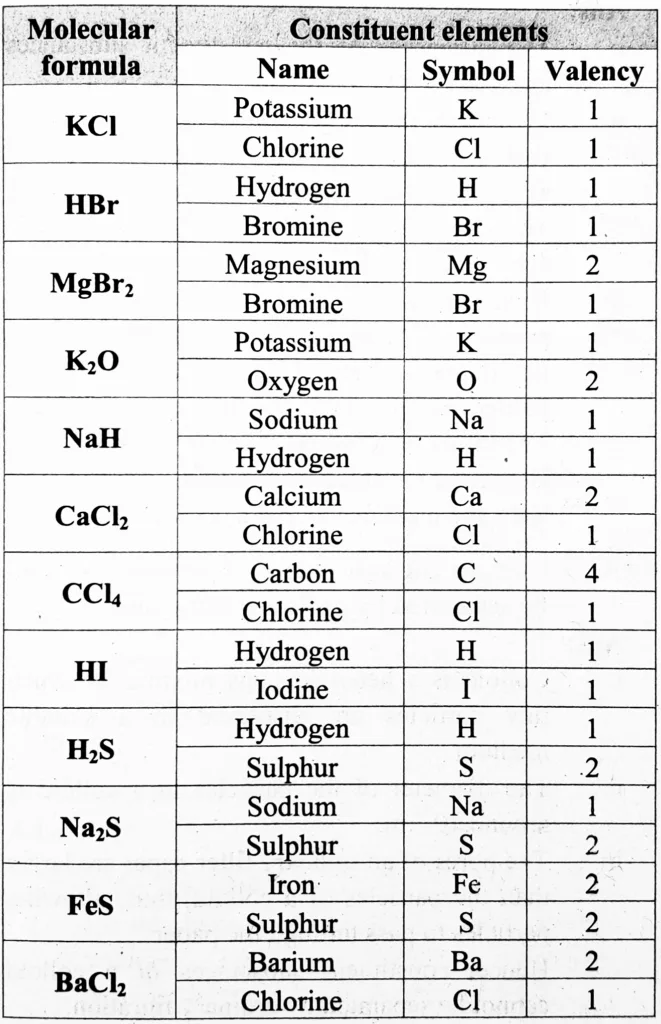
5. Write the names and symbols of the constituent elements and identify their valencies from the molecular formulae given below.
KCl, HBr, MgBr₂, K₂O, NaH, CaCl₂, CCl₄, HI, H2S, Na₂S, FeS, BaCl₂
Ans:
6. Chemical composition of some matter is given in the following table. Identify the main type of matter from their.

Ans:

7. Write scientific reason.
a. Hydrogen is combustible, oxygen helps combustion, but water helps to extinguish fire.
Ans:
(i) The properties of a compound are different from those of the constituent elements.
(ii) Water is a compound of oxygen and hydrogen.
(iii) Hydrogen gas is combustible, and oxygen gas supports combustion. However, the properties of water are different, as it is neither combustible nor does it support combustion. Instead, it is used to extinguish fire.
(iv) Hence, hydrogen is combustible, oxygen helps combustion, and water helps extinguish fire.
b. Constituent substances of a colloid cannot be separated by ordinary filtration.
Ans:
(i) A colloid is a heterogeneous mixture in which tiny particles are dispersed in a suitable medium.
(ii) The diameter of the particles in a colloid is around 10 m.
(iii) The pores of ordinary filter paper are larger than the particles of a colloid, thus allowing particles to pass through the paper.
(iv) Hence, the constituent substances of a colloid cannot be separated by ordinary filtration.
c. Lemon sherbat has sweet, sour and salty taste and it can be poured in a glass.
Ans:
(i) The properties of the constituent substances are retained in the mixture.
(ii) Lemon sherbat is a homogeneous mixture of various ingredients, such as lemon juice, sugar, salt, etc., dissolved uniformly in water. Therefore, lemon sherbat has a sweet, sour, and salty taste.
(iii) In lemon sherbat, water is present in large proportion. Therefore, lemon sherbat exists in a liquid state. Water is a liquid and can be poured, as it possesses the property of fluidity. Therefore, lemon sherbat can be poured.
(iv) Hence, lemon sherbat has a sweet, sour, and salty taste, and it can be poured into a glass.
d. A solid matter has the properties of definite shape and volume.
Ans:
(i) The strength of intermolecular force is very strong in the solid state of matter.
(ii) As a result, the particles of solid are very close to each other, and they vibrate at their fixed positions. The particles cannot move freely and occupy the available space.
(iii) Hence, a solid matter has the properties of definite shape and volume.
8. Deduce the molecular formulae of the compound obtained from the following pairs of elements by the cross multiplication method.
a. C (Valency 4) & Cl (Valency1)
Ans:
Step 1: Write the symbols of the constituent elements.
C Cl
Step 2: Write the valency below the respective element.
C Cl
4 1
Step 3: Cross multiply to obtain the number of atoms of the constituent elements in the molecule of the compound.

Step 4: Write the formula of the compound obtained by cross multiplication.
CCl₄
b. N (Valency 3) & H (Valency 1)
Ans:
Step 1: Write the symbols of the constituent elements.
N H
Step 2: Write the valency below the respective element.
N H
3 1
Step 3: Cross multiply to obtain the number of atoms of the constituent elements in the molecule of the compound.
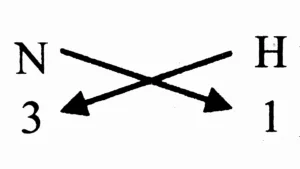
Step 4: Write the formula of the compound obtained by cross multiplication.
NH₃
c. C (Valency 4) & O (Valency 2)
Ans:
Step 1: Write the symbols of the constituent elements.
C O
Step 2: Write the valency below the respective element.
C O
4 2
Step 3: Cross multiply to obtain the number of atoms of the constituent elements in the molecule of the compound.

Step 4: Write the formula of the compound obtained by cross multiplication.
C₂O₄
Step 5: The number of constituent atoms in the final molecular formula should be the smallest possible whole numbers. So, divide the formula obtained in step 4 by ‘2’ and write the final molecular formula of the compound
CO₂
d. Ca (Valency 2) & O (Valency 2)
Ans:
Step 1: Write the symbols of the constituent elements.
Ca O
Step 2: Write the valency below the respective element.
Ca O
2 2
Step 3: Cross multiply to obtain the number of atoms of the constituent elements in the molecule of the compound.

Step 4: Write the formula of the compound obtained by cross multiplication.
Ca₂O₂
Step 5: The number of constituent atoms in the final molecular formula should be the smallest possible whole numbers. So, divide the formula obtained in step 4 by ‘2’ and write the final molecular formula of the compound
CaO
