Chapter 1 - Historiography : Development in the West
1. (A) Choose the correct option from the given options and complete the statement.
(1) It may be said that …….. was the founder of modern historiography.
(a) Voltaire
(b) René Descartes
(c) Leopold Ranké
(d) Karl Marx
Ans: Option (a) – Voltaire
(2) ………… wrote the book entitled ‘Archaeology of Knowledge’.
(a) Karl Marx
(b) Michel Foucault
(c) Lucien Febvre
(d) Voltaire
Ans: Option (b) – Michel Foucault
(B) Identify and write the wrong pair in the following set.
(1) Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel – ‘Reason in History’
(2) Leopold von Ranké – ‘The theory and Practice of History’
(3) Herodotus – ‘The Histories’
(4) Karl Marx – ‘Discourse on the Method’
Ans: The wrong pair is:
Karl Marx – ‘Discourse on the Method’
Explanation: ‘Discourse on the Method’ was written by René Descartes.
2. Write short notes.
(1) Dialectics
Ans:
(i) According to Hegel, grasping the meaning of any event happens in terms of two direct opposites.
(ii) Human mind cannot understand the true nature of that event, without understanding the opposites.
For example; True-False, Good-Bad, etc.
(iii) In order to understand the true nature of a thing, one needs to know both true and false, similarly good and bad.
(iv) This method of analysis, which is based on opposites, is known as ‘dialectics’.
(2) Annales School
Ans:
(i) Annales School was started by French historians in the 20th century.
(ii) It gave a new direction to history writing.
(iii) It was recognized now that history was not only about political events, kings, and leaders but also about climate, people, agriculture, trade, technology, means of communication, social divisions and their psychology, etc.
3. Explain the following with its reason.
(1) Historical research was driven to focus in depth on various aspects of women’s life.
Ans:
(i) The writings of Simone-de-Beauvoir helped in establishing the fundamentals of feminism.
(ii) The feminist historiography emphasised not only on the inclusion of women in history but also on the rethinking of the male dominated perspective of history.
(iii) As a result historical research was driven to focus in depth on various aspects of women’s life, such as their employment, their role in trade unions, institutions working for their cause, their family life, etc.
(2) Foucault called his method, ‘the archaeology of knowledge’.
Ans:
(i) Foucault drew attention to the fact that archaeology does not strive to reach the ultimate historical truth but attempts to explain various transitions in the past.
(ii) He felt that explaining the transition in history is more important than arranging historical events in chronological order.
(iii) Foucault supplemented his method of historical analysis by including unacknowledged areas such as psychological disorders, science of medicine, prison administration, etc.
(iv) Hence this method is called ‘the archaeology of knowledge’.
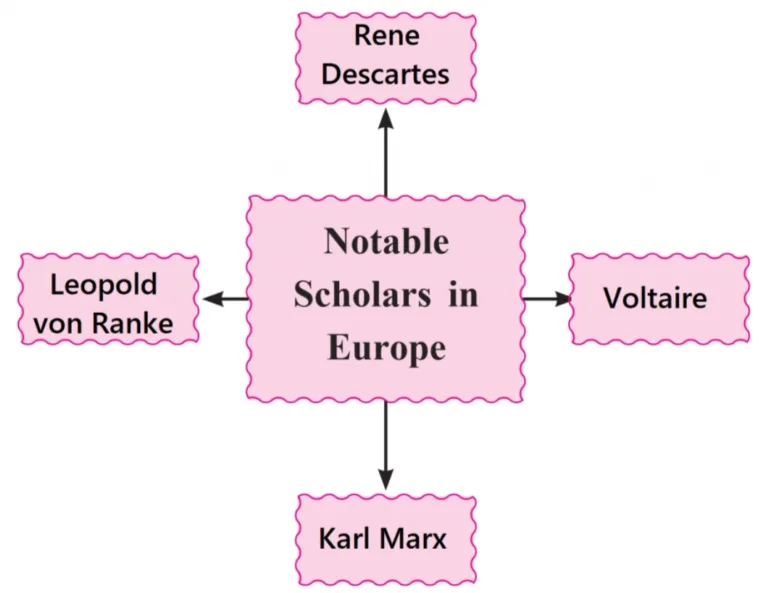
4. Complete the concept chart.
Ans:
5. Answer the following in detail.
(1) Explain Karl Marx’s ‘Class Theory’.
Ans:
(i) According to Karl Marx, history was not about abstract ideas, it was about living people.
(ii) Human relationships were shaped by the fundamental needs of people and their ownership as well as nature of the prevalent means of production to meet those needs.
(iii) The accessibility of these means to different strata of society may not be equal.
(iv) This inequality causes a division of society into classes, leading to a class struggle.
(v) The class that owns the means of production economically exploits the rest of the classes.
(2) What are the four characteristics of modern historiography ?
Ans:
(i) Its method is based on scientific principles. It begins with the formation of relevant questions.
(ii) These questions are about the deeds of the members of societies of a particular period. History does not suggest any interrelation between divine and human deeds.
(iii) Answers to these questions are supported by reliable evidence.
(iv) History presents a graph of mankind’s journey with the help of past human deeds.
(3) What is feminist historiography?
Ans:
(i) The restructuring of history from the perspective of women is called as feminist historiography.
(ii) Feminist historiography emphasized not only on the inclusion of women in history but also on rethinking the male-dominated perspective of history.
(iii) It drove historical research to focus in depth on various aspects of women’s life such as their employment, their role in trade unions, institutions working for their cause, their family life, etc.
(iv) In historical writing after 1990, women were portrayed as an independent social class.
(4) Explain Leopold von Ranké’s perspective of history?
Ans:
(i) Leopold Von Ranké criticized’ imaginative narration of history.
(ii) He emphasized on information gathered through original documents.
(iii) He also stated that all types of documents associated with a historical event need to be examined with the greatest care.
(iv) He believed that with this method it was possible to reach the historical truth.
